What are NR, NIC & STC?
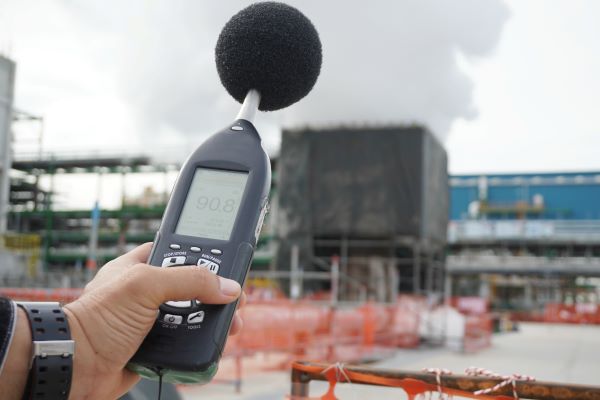
The overall air-borne sound isolation between two adjacent spaces is measured by the NR (Noise Reduction) between the spaces, and is rated by the single number NIC value (Noise Isolation Class). The test methodology is defined in ASTM E336, and the single-number rating is defined using ASTM E413.
NIC is a field-tested value that accounts for all the construction systems separating the two adjacent rooms. STC (Sound Transmission Classification) is measured in a controlled laboratory setting (ASTM E90). The lab test setting discounts construction variables such as absorption in the receiving room, partition size, and flanking paths.
ASTC (Apparent Sound Transmission Classification) is also a field measured rating using the test method from ASTM E336. Although both field tests, ASTC and NIC differ through the implementation or reverberation time and absorption. ASTC follows the ATL (Apparent Transmission Loss) equation (Eqn. 1 ASTM E336) which is similar to the NNR (Normalized Noise Reduction) equation (Eqn. 2 ASTM E336). NNR is equivalent to NR plus the addition of a reverberation correction factor, based on the measured reverberation time in the room. NR is simpler, and corresponds to basic TL (Transmission Loss).
Calculating Noise Isolation Class (NIC)
Rated partition STC values can be converted to overall sound isolation using the following equation:
NIC = STC – 10log(S/A)
- S = surface area of partition (ft2)
- A = amount of absorption in the receiving room (Sabins), averaged over octave bands 125Hz to 4000Hz
- Based on the NRC (Noise Reduction Coefficient) and square area of all room finishes.
The design STC should be up to 5 points higher than the required NIC for partitions with adjacencies that have little absorption (ballrooms, exam rooms). The design STC should = NIC for rooms w/ high absorption (guestrooms, private offices).