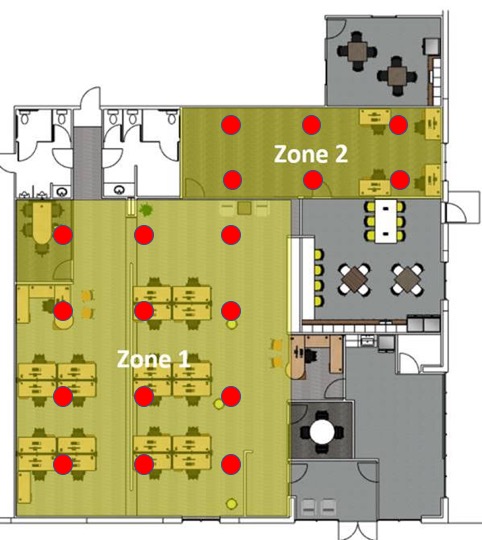
Sound Masking systems are best used in open areas where distracting noises can make it difficult to focus or relax. This is commonplace in open offices and bullpens, as well as call centers and libraries. Sound masking provides speech privacy in the space, so that employees can focus in the office without annoying and distracting background noise.
Where are the Speakers installed?
Most sound masking systems are designed to install the speakers up in the plenum space. This keeps them out of sight, and out of mind – the ideal application provides speech privacy without workers even realizing that the speakers are there.
Sound Masking speakers are commonly placed 15 ft apart, as they generally cover 225 square feet each. They are spaced at approximately 7 feet from the nearest wall, and spacing must be adjusted for the length and width of the room, as well as any irregular jut-outs or shapes.
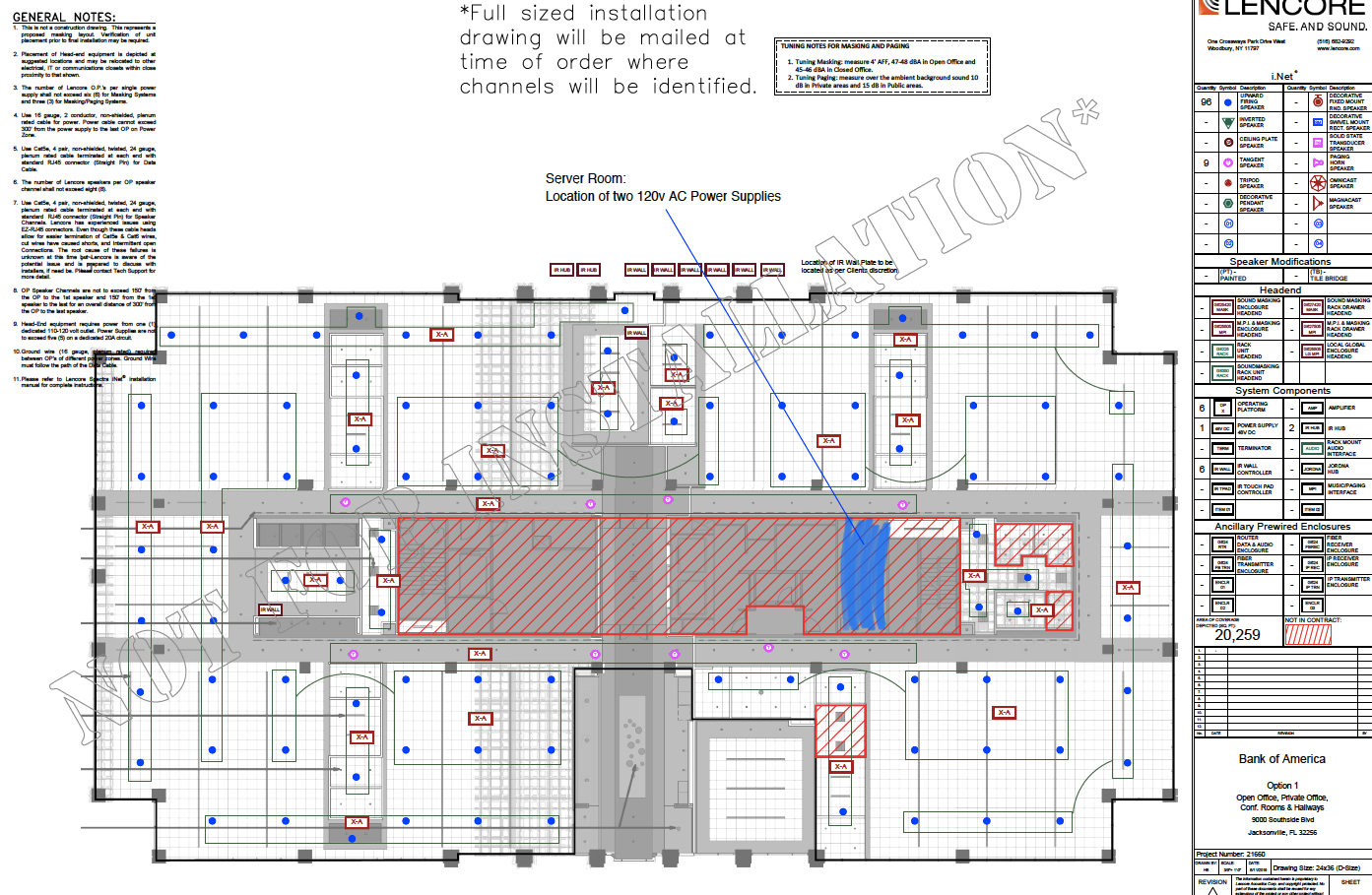
However, the exact spacing of the speakers depends on a number of factors, including the height of the plenum, the height of the ceiling, as well as the thickness of the ceiling tile.
See a standard tuning guide below, as well as two common sound masking speaker layouts.
NOTE: All sound masking installations should be completed by a low voltage certified installer.
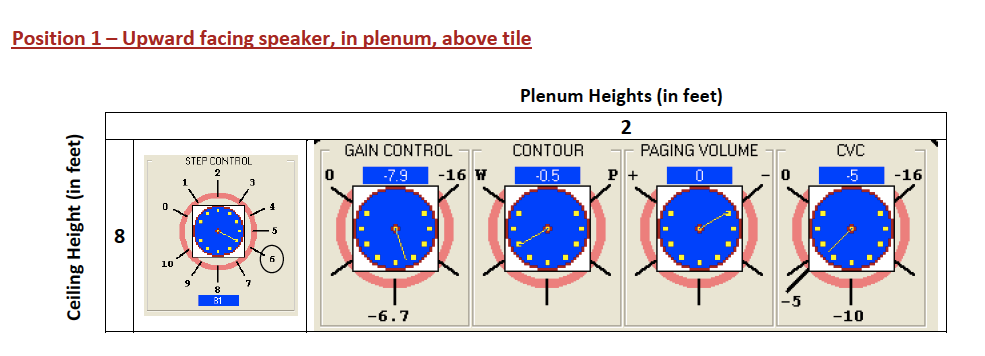
Sound masking speakers must be tuned and balanced in the field, looking for two things.
- First, the white noise to pink noise spectrum must be adjusted depending on the CAC value of the tiles. If it isn’t exposed deck, pink noise should be played because that is what will be heard below. However, if there is a thick ceiling tile then White Noise should be played since the ceiling tiles will scrape out, or block, the high-frequency noises of the white noise and leave a pink noise below.
- Secondly, the white noise speaker should be placed and tuned so that the average DBA level at 4.5 feet from the ground is 43 DBA in a closed office and 45-47 DBA in an open office. Experienced sound masking technicians will be able to walk around with a calibrated decibel meter in determine if there are hot or cold spots on the floor.
How are Sound Masking speakers wired?
Sound Masking systems are generally wired with 12-2 and 12-5 plenum-rated wire to ensure that they receive 24-volt power.
CAT5E may be needed for more advanced systems that are to be controlled at a central control panel. This allows for controlling of zones over IP, and minimizes re-work needed if offices are reconfigured in the future.
For large buildings that require mass notification, additional redundancies may be required, and self-healing capabilities to ensure that all speakers are online in the case of an emergency.
As noted above, low-voltage technicians, such as those at Commercial Acoustics, are capable of ensuring proper routing and cabling techniques required in new construction or retrofits.
For More Information See: Sound Masking Case Studies
Summary: Sound Masking System Installations & Design
Sound Masking systems are simply the ability to use white or pink noise in an open space to provide improved speech privacy and acoustic comfort. By properly spacing and wiring the sound masking speakers, then performing a fine-tuning and balance, the end client receives a system that greatly reduces noise complaints.